SPP2 - Lesson 5: The Business Case
in this lesson we will cover the Project Business Case
Subjects covered in the lesson:
Develop Project Charter
Purpose of BC theme
Business Case defined
The P2 approach to the Business Case
Purpose of Business Case
Composition of Business Case
Derivation
Format and Presentation
Quality Criteria
There are n videos in this lesson:
Introduction
Defining Project (Management)
- One of a Kind
- Temporary
- Constrained
- Change
- Cross Functional
- Uncertainty
- Knowledge
- Skills
- Techniques
- Tools
- ATTITUDE
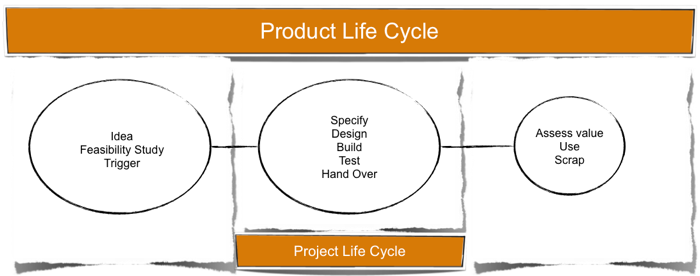
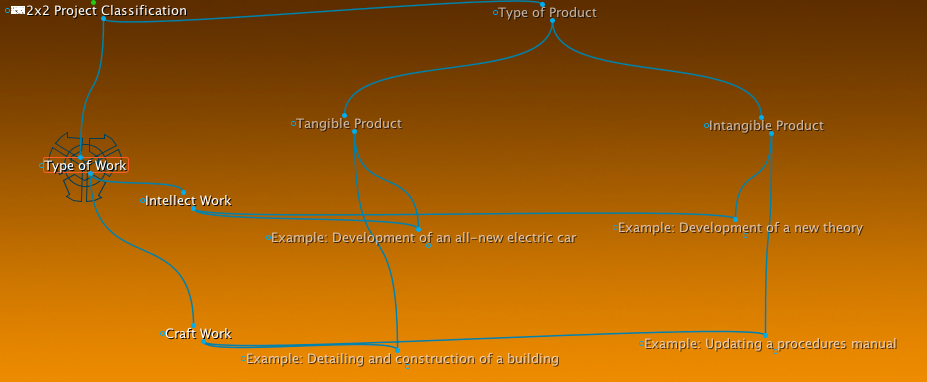
Project Types
- Type of work
- Craft
- Intelect
- type of Product
- Tangible
- Intangible
- Level of Uncertainty
- Level of Complexity
- Level of Pace
- Culture
- Application area / Industry
- Life-cycle stage
- Strategic Importance
Project Success
Key Characteristics of Prince2
- Public Domain
- Based on Best Practices
- Common Project Language
- Certifications
- Foundation
- Practioner
Benefits of Prince2
- Better planning and communication
- Can be applied to any type of project
- Clarity of Roles and Responsibilities
- Consistency
- Easy assessment
- Management by exception
- Promotes learning
- Proven Best practice for projects governance
- Results oriented not task oriented
- Widely Recognized
Structure of Prince2
Prince2 Principles
- Business Justification
- Learn from experience
- Manage by exception
- Manage by stage
- Product focus
- Roles and responsibilities
- Tailor
2.1 Continued Business Justification
A PRINCE2 project has continued business justification.
A requirement for a PRINCE2 project is:
- There is a justifiable reason to start it
- The justification should remain valid throughout the life of the project.
The justification can change!
And as a result the project objectives/deliverables may change!
The justification is documented and approved
DON'T start a project without business justification
STOP the project when there no longer is
a valid business justification
2.2 Learn from experience
PRINCE2 project teams learn from previous experience: lessons are thought, recorded and acted upon throughout the life of the project.
- When starting a project
- As the project progresses
- As the project closes
This needs to be a proactive principle. IOW, don't wait for someone else to tell.
Lessons can be learned on multiple levels. Individual, team, project, organization.
Remember that past success is no guarantee for future success.
Also be aware of the Knowing - Doing Gap.
2.3 Defined Roles & Responsibilities
A PRINCE2 project has defined and agreed roles and responsibiities within an organization structure that engages the business, user and supplier stakeholder interests.
All projects have the following primary stakeholders:
- Business Sponsors
- Users
- Suppliers
the business/sponsor owns the project. A project is done on behalf of the business, its purpose is to fulfil a certain business objective. The business has to make a choice whether to fund a project fund another project or just bank the money.
The outcome of a project will be used by the user. It is therefore important that the user is represented on the project board.
The outcome of the project is produced by the supplier. This can be either a internal or external supplier.
2.4 Manage by Stages
A PRINCE2 project is planned, monitored and controlled on a stage-by-stage basis.
PRINCE2 overcomes the planning horizon by:
Dividing the project into a number of management stages
Having a high level project plan and a detailed stage plan
Planning, delegating, monitoring and controlling the project on a stage-by-stage basis
A management stage is not the same as a production stage.
P2 requires there to be a minimum of 2 management stages:
Initiation stage
(further) management stage(s)
Note that Starting Up a project (SU) is NOT a management stage!
2.5 Manage by Exception
"No news is good news"
This can only be achieved when there is sufficient planning and information available. It does require a new, or adjusted, attitude by all parties involved.
2.6 Product Focus
A task without a specific deliverable is meaningless. In the end of the day projects produce products.
2.7 Tailor to suit the project environment
Themes
- Business Case
- Change
- Organization
- Plans
- Progress
- Quality
- Risk
Processes
- 1: Starting up a Project (SU)
Projects don't fall out of thin air even if that may seem like that sometimes. The likelihood of project success is significantly improved when after completing a thorough project startup. In this section Starting up a project we will explain in detail the following 4 elements- 2: Directing a Project (DP)
- 3: Initiating a Project (IP)
- 4: Controlling a Stage (CS)
- 5: Managing Project Delivery (PD)
- 6: Managing a Stage Boundary
- 7: Closing a Project (CP)
- # Change
- Product based planning (PBP)
- Quality Review
- Thoughts = 65
- Links = 73
- Notes = 19
Tailoring PRINCE2 to the project environment
Prince2 (P2), Techniques
Downloads
{iframe width="750" height="800"}http://ambidexter.ca/P2-Training{/iframe}
The Brainzip that was shown in the video can be downloaded by clicking on the link below:
Note that only paying customers have access to the Brainzip that includes the attachments (Icons)
Brainzip Statistics: